
by dse19 | Nov 20, 2023 | Uncategorized
Introduction
Imagine you have a business of your own. Consider it a dream come true to have it thrive. Now, as an entrepreneur, what would you care about most for your business’s future? As a matter of fact, you can respond to this question with a multitude of answers, and all of them will converge to having a viable business, which becomes so through profits, which are achieved through SALES!
For the purpose of realizing the importance of sales to a business, we dive in this blog into the sales performance of a US based company belonging to the food and beverage sector and operating its three contemporary coffee-shop like stores within the busiest state in the United States, New York.
The company has 4 facilities, 1 main office and 3 customer facing stores (store 2, 3, and 4).
Overall Sales Performance
Our focus is to dissect and understand the sales trends and patterns that have emerged over the past two years, shedding light on the company’s growth, challenges, and opportunities.
The company’s sales trajectory exhibited a notable improvement in the first half of the years 2017 to 2018, indicating a successful adoption of growth strategies during this period. However, an interesting pattern emerged in the latter half of these years. The sales figures, initially showing distinct growth, began to converge towards approximately the same numbers in the second halves of both years. This dichotomy of divergence and subsequent convergence underscores the necessity to dig deeper into the analysis, understanding the underlying factors that led to this trend and identifying strategies to ensure consistent growth during upcoming years.
Sales Performance by Store
To further our understanding of the underlying patterns, rather than aggregating results of all stores, the sales performance of each store is studied separately throughout 2017 and 2018, offering a meticulous examination of sales figures, customer demographics, and quarterly trends. The objective is to uncover hidden challenges and propose a comprehensive action plan for sustained improvement.
Inadequacy of Store 2 Performance
In 2017, Store 2 reported sales of $281,000, which experienced a positive growth trajectory, reaching $322,000 in 2018. While indicative of progress, it’s essential to juxtapose these figures with the more robust performances of Store 3 and Store 4, recording $555,000 and $564,000 in 2017, and $637,000 and $638,000 in 2018, respectively.
In our analysis of growth percentages, Store 2 demonstrated a notable growth rate of approximately 14.6%. This rate is closely aligned with the growth rates of Stores 3 and 4, which reported rates of approximately 15% and 13%, respectively. However, it’s important to clarify that while Store 2’s growth percentage is similar to that of Stores 3 and 4, the key distinction lies not in these percentages, but in the actual growth amounts measured in US Dollars. This crucial aspect will be further explored in our upcoming detailed analysis.
While Store 2 is on a positive growth trajectory, there’s an evident opportunity to fortify its position by strategizing to match the sales amounts of its counterparts.
Customer Demographics and Value
The company’s overarching target demographic is the 40-60 age group, a segment known for its purchasing power and brand loyalty as shown in the below visualization. This age group forms the core customer base across all company stores.
However, when delving into the performance specifics, it becomes evident that Store 2 is underperforming in engaging this crucial demographic compared to its sister stores.
A closer look at customer value reveals intriguing patterns. The consistent presence of 2,131 low-value customers (smaller transactions in amount) across all stores and both years raises the question of whether there’s untapped potential among this segment. Concurrently, the identification of 119 high-value customers (larger transactions in amount) accentuates an opportunity for targeted strategies to cultivate and retain these valuable patrons.
In Store 2, a specific area of concern is the notably weak number of low-value customers compared to other stores. Addressing this issue is crucial for the store’s overall performance.
New Customer Acquisition
Store 2 consistently attracted fewer new customers each month compared to the more robust acquisition rate observed at Store 3. With respect to store 4, it is attracting the lowest number of customers per month; nevertheless, the impressive performance of store 4 suggests it is approaching market saturation, much faster than store 2.
The gap in new customer acquisition at Store 2 signals an urgency to investigate and enact strategies aimed at elevating foot traffic and expanding the customer base.
Monthly Purchase per Visiting Customer
Store 2’s performance in terms of monthly purchase per visiting customer presents a notable area for improvement. Store 2 records the lowest customer contribution among its counterparts. This finding is particularly concerning when juxtaposed with the stronger performance of Stores 3 and 4 in the same metric.
The need for improvement in monthly purchase per customer at Store 2 highlights potential areas for strategic intervention. Focusing on upselling and enhancing the overall in-store experience could be key in encouraging customers to spend more during each visit. Addressing this gap is crucial for Store 2 to not only align with the performance of its sister stores but also to optimize its revenue potential from every customer interaction.
Proposed Solutions Overview
Boosting Store 2’s market presence requires innovative and effective strategies. Here, a three-pronged approach is presented: an engaging social media campaign, impactful influencer collaborations, and a customer-enticing loyalty program. Each strategy is crafted to not only enhance brand visibility but also to deepen customer engagement and drive sales.
1. Social Media Campaign
- Objectives: Increase brand awareness on Instagram, Facebook, Twitter; drive online traffic to Store 2.
- Strategy: Post visually engaging content, use polls and quizzes, encourage user-generated content.
- Schedule: Regular, strategically timed posts; use a unique campaign hashtag for visibility and engagement.
2. Influencer Collaboration
- Criteria: Select local influencers aligned with Store 2’s image.
- Terms: Offer exclusive promotions for influencers’ followers; request content showcasing products.
- Performance: Track success using referral codes/links and engagement metrics.
3. Loyalty Program
- Components: Points system for purchases, exclusive discounts, personalized offers.
- Launch: Announce via social media, email, and in-store materials; use in-store signage for visibility.
- Staff Involvement: Train staff to engage customers about the program and provide technical support.
Recommendations
Elevating Store 2’s success hinges on a mix of dynamic strategies: targeted seasonal marketing, establishing a customer feedback loop, forming strategic local partnerships, leveraging data-driven decision-making, and enhancing the in-store experience. These approaches aim to boost sales, expand the customer base, and improve overall satisfaction. This segment delves into how each method can effectively transform Store 2’s business approach.
1. Seasonal Marketing Strategies
Develop seasonal marketing campaigns to capitalize on peak shopping periods and mitigate sales fluctuations. Tailor promotions and incentives to match customer behaviours during different quarters.
2. Customer Feedback Loop
Establish a robust feedback loop to gather insights from customers on their seasonal preferences and expectations. Leverage this feedback to tailor products and services to seasonal demands.
3. Collaborative Partnerships
Explore partnerships with local businesses and influencers to create synergies that drive foot traffic and broaden the customer base.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
Invest in data analytics tools to gain deeper insights into customer behavior. Utilize this data to make informed decisions on product placement, pricing, and marketing strategies.
5. In-Store Experience Enhancement
Investigate and enhance the in-store experience, considering factors such as store layout, ambiance, and product presentation. An inviting and immersive environment can positively impact customer perception and satisfaction.

by ars23 | Nov 20, 2023 | Uncategorized
What is your value?
Although you would like to say you cannot be measured by a number, you are! Studies implemented to assess projects and decide whether to implement them or not reduce you to a number, just like they judge the value of a building.
The world is heading in a clear direction: focus on development! Although, it seems like a great thing, easing our lives, take a minute to explore its impact:
We can notice how the more developed countries have, in general, higher suicide rates each year, especially more recently. To demonstrate this further, we take a look at the following visualization comparing average suicide mortality rate (per 100,000 population) per given years across the main regions we are considering:
What is the point?
The point is that we should put more emphasis on our well-being and our connection with the world instead of only focusing on materialistic development. Whenever we take action on something, we must evaluate the impact, and in the case of development, the signs are not good.
However, it is not too late to make a change. Bhutan, the happiest country in the world, prioritizes the mental well-being of its citizens. It is the only country that uses the gross national happiness indicator (GNH) just like other countries focus on the gross national income.
The following visualization shows the average suicide rate per country instead of region:
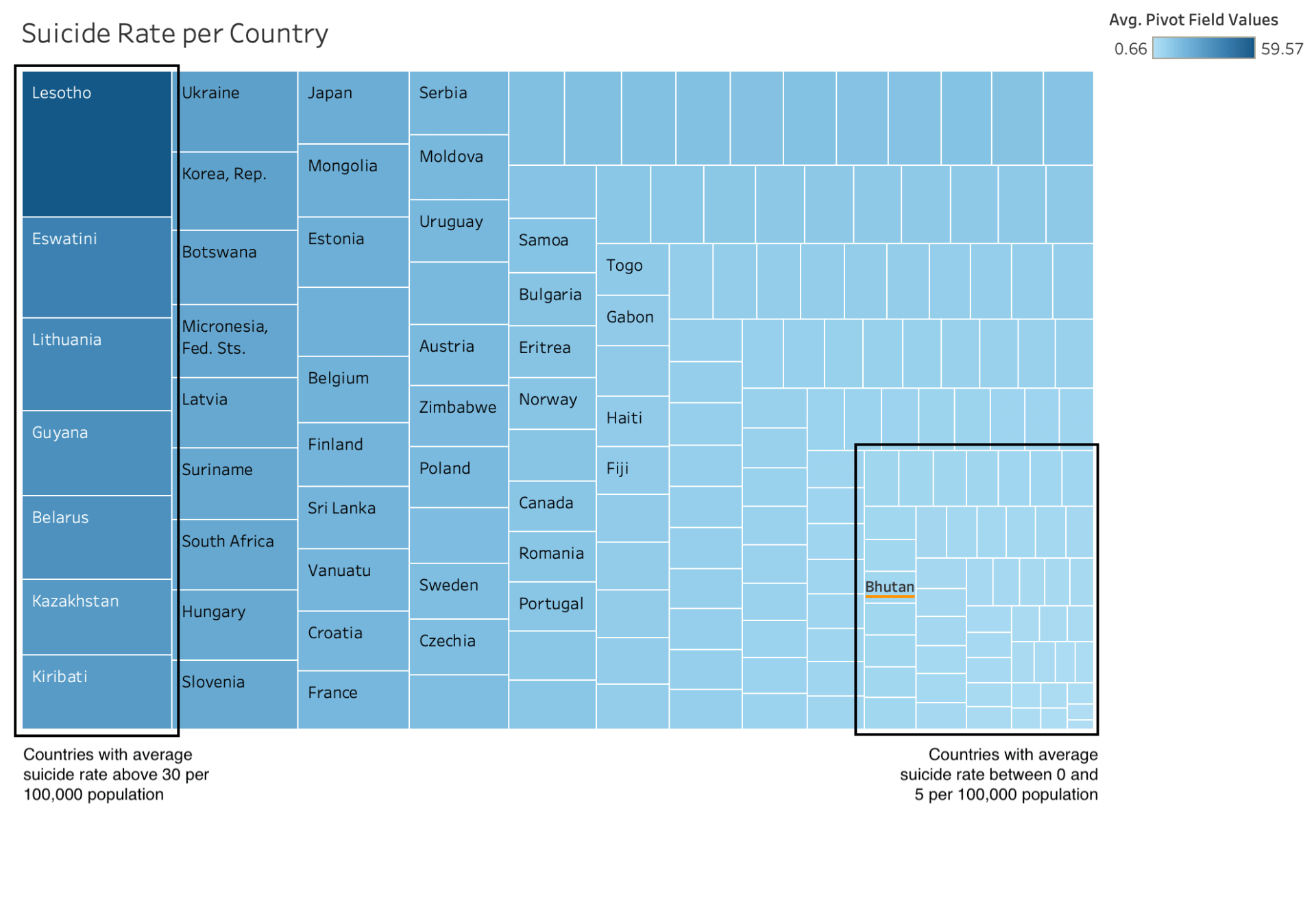
Notice how Bhutan falls in the range of countries that average from 0 to 5 suicide per 100,000 population compared to other countries that average more than 30 in the range of given years (2000-2019).
We recommend people to prioritize their well-being and mental health, but most importantly, governments to realize that economic and materialistic development is not yielding that wanted outcome. To prioritize humanity, governments ought to start taking GNH into consideration with every decision they are making.
Let us choose humanity!
by hfc03 | Nov 20, 2023 | Visualization
The Initial Divide (1994):
In 1994, Tunisia’s electrification landscape presented a striking contrast. Urban areas were almost entirely electrified at 99.87%, but rural regions lagged significantly with only 66.29% access. This gap underscored a larger issue of inequality in access to basic utilities.
The Transformation Journey:
A visual representation, through a two-line chart, illustrates this journey vividly. As the years progressed, a noticeable shift occurred. The lines representing rural and urban electricity access started converging. This wasn’t just infrastructural progress; it was a story of reducing disparity and fostering inclusivity.
Achieving Parity (2016 Onwards):
By 2016, an impressive feat was achieved: both rural and urban areas reached a 100% electrification rate. This landmark achievement was the culmination of a series of strategic initiatives, reflecting Tunisia’s steadfast commitment to equitable development.
Behind the Success:
The road to this success was paved with innovative strategies and strong political will. Implementing technologies like photovoltaic cells in remote areas exemplified the innovative approach to overcoming geographical and logistical challenges.
Conclusion – A Model for the Future:
Tunisia’s electrification story is not just about lighting up homes; it’s about empowering communities, ensuring equitable access to essential services, and setting a precedent for other nations facing similar challenges. It’s a narrative that demonstrates how vision, commitment, and innovation can transform a nation.
Let’s keep this conversation going! What are your thoughts on such transformative initiatives?

by nmm51 | Nov 20, 2023 | Uncategorized
In the challenging landscape of global unemployment, the story of Youmna, a 30-year-old Egyptian woman, stands as a poignant example. A decade of dedication to her organization abruptly ended due to the pandemic, plunging her into a three-year job search. This narrative, compounded by a lack of early educational opportunities, resonates as a common experience in the Arab world.
At its core, Youmna’s story grapples with unemployment, a conflict explored through its definition and the consequences it imposes on individuals, societies, and economies. Her personal struggles, marked by stress-related health issues, mirror the toll exacted on individuals. Societal repercussions manifest in limited opportunities, substandard living conditions, and underfunded institutions.
Global unemployment rates expose a stark reality, with the Arab region leading at 11.26%, underscoring the urgency of addressing the issue. The intricate relationship between education and unemployment becomes apparent, with studies confirming that higher education levels correlate with lower unemployment risks. A comparative graph illustrates Brazil’s struggle with basic and intermediate education versus Japan’s success with advanced education.
A potential solution emerges: investing more in education to elevate citizens’ skills and foster innovation. Aligned with Sustainable Development Goal 4, advocating for quality education becomes imperative. The graph depicting average education expenditure across countries emphasizes that nations with lower unemployment rates allocate more resources to education. The recommendation is clear: countries should prioritize and increase spending on their education systems, creating a pathway to innovation, economic growth, and enhanced employment opportunities.
Youmna’s narrative encapsulates the broader struggle against unemployment. The call to action is unmistakable: invest in education to reshape the narrative, empower individuals, and build resilient, thriving communities. In the transformative power of education lies the resolution to Youmna’s journey, a beacon of hope in the face of adversity.

by cjk08 | Nov 20, 2023 | Uncategorized

Introduction:
In 2007, the world experienced a financial shockwave that originated from the U.S. housing market downturn. The crisis quickly rippled across global economies, with significant impacts felt in the U.S., U.K., and China. In this post, we’ll explore a comprehensive analysis of the crisis and the concerted policy responses that helped navigate these turbulent economic waters. Accompanied by insightful Tableau visualizations, we delve into the monetary and fiscal adjustments that shaped the path to recovery.
The Epicenter of the Crisis:
The 2007 financial crisis is a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of global markets. Starting in the U.S., the collapse of the housing bubble sent shockwaves that were felt in the U.K., a major financial hub, and China, the burgeoning economic powerhouse. The crisis highlighted vulnerabilities and sparked a global debate on economic safeguards. Our Tableau visualizations, which I’ll share throughout this post, bring to life the data behind these seismic economic shifts.
Economic Indicators in Turmoil:
GDP Growth Rate: The severe downturn in the U.S. and UK economies in 2009, with GDP growth plummeting to -2.60% and -4.51%, respectively, signified deep recessions. China’s maintenance of a 9.40% growth rate, despite a global slowdown, demonstrated the effectiveness of its economic policies and a less interconnected reliance on global financial systems.
Unemployment: The dramatic rise in U.S. unemployment to 9.25% in 2009 mirrored the harsh reality of the economic crisis’s impact on the labor market. The UK’s unemployment rate’s more moderate increase to 7.54% indicated a resilient but strained job market. China’s steady unemployment rate suggested a controlled labor environment, possibly cushioned by government-led initiatives.
Inflation and Deflation: The pivot to deflation in the U.S. and China in 2009 highlighted the breadth of the economic contraction, marked by plummeting consumer demand. The UK’s decreasing inflation rate, from its 2008 peak, nonetheless remained positive, reflecting persistent cost pressures despite a contracting economy.
Investor Sentiment and Market Response:
FDI: The UK’s steep decline in FDI following the crisis suggested capital flight and a significant erosion of economic confidence, a contrast to the U.S.’s more stable investment climate. China’s gradual FDI decline mirrored the broader cautious stance of global investors during the period of uncertainty.
Equity Markets: The UK and U.S. equity markets’ deep dives of -49.5% and -38.5% in 2008, along with China’s -52.7% plunge, captured the panic and rapid revaluation of future earnings potential, significantly affecting wealth and spending.
Monetary & Fiscal Adjustments: Navigating Through Economic Turbulence
The global financial crisis of 2007-2008 forced countries to reevaluate their monetary and fiscal strategies. Central banks across the world slashed interest rates, while governments ramped up borrowing to inject liquidity and stimulate economic activity. The graphs provided offer a glimpse into how China, the United Kingdom, and the United States adjusted their policies in the face of economic headwinds.
Monetary Policy Adjustments: A Dive into Negative Real Interest Rates
In response to the financial crisis, China, the UK, and the US adopted aggressive monetary policies, including steering real interest rates into negative territory to encourage borrowing and investment. This is particularly evident in 2009’s negative real interest rates.
China responded to the crisis by lowering its real interest rates from -0.260 in 2007 to -2.306 in 2008, indicating a decisive move to encourage spending and investment.
The UK followed a similar path, with real interest rates dropping from 3.106 in 2007 to -1.241 in 2009, reflecting a substantial monetary stimulus.
The US saw its real interest rates decrease from 5.207% in 2007 to 2.592 in 2009, as part of its strategy to revive the economy.
Fiscal Stimulus: The Path of Increased Government Debt
The fiscal response to the crisis was marked by an increase in government debt, as seen in the upward trend of central government debt relative to GDP. This increase is indicative of a commitment to boost economic activity through government spending.
The UK’s central government debt rose sharply from 93.63% in 2007 to 130.69% in 2010, a clear sign of significant fiscal intervention.
The US also saw its government debt climb from 63.82% in 2007 to 84.96% in 2010, as it took on more debt to stabilize the economy.
For China, although not displayed on the graph, the World Bank and IMF data show an increase in central government debt from 16.4% in 2007 to 33.5% in 2010, demonstrating China’s use of fiscal policy to maintain economic momentum.
Analyzing the Impact of Policy Adjustments on Economic Indicators:
Following these adjustments, we look at how they influenced key economic indicators. The equity markets in all three countries showed signs of recovery in 2010, with China’s market increasing by 8.2%, the UK’s by 12.8%, and the US’s by 13.6%. Such improvements in the equity markets typically reflect greater investor confidence, potentially buoyed by lower interest rates making equities more attractive compared to fixed-income assets.
In terms of foreign direct investment (FDI), there was a noticeable uptick in all three countries. China’s FDI as a percentage of GDP went up by 55.9%, the UK’s by an impressive 345.2%, and the US’s by 57.7%. The growth in FDI highlights the global improvement in investor sentiment and market confidence, likely influenced by the monetary easing and fiscal stimulus measures.
As for GDP growth, all three countries experienced positive changes. China continued its robust growth; the UK and the US both rebounded from negative growth rates in 2009 to positive rates in 2010. These changes underscore the effectiveness of the stimulus efforts, which aimed to encourage borrowing, spending, and overall economic activity.
Findings and Recommendations:
The economic data from the 2007-2008 financial crisis reveal that while aggressive monetary easing and fiscal stimulus were critical in mitigating the downturn, the recovery trajectory varied significantly across nations. The U.S. and the UK, with deep contractions in GDP and spiking unemployment, required robust policy responses to revive consumer confidence and stabilize financial markets. On the other hand, China’s proactive fiscal measures, particularly in infrastructure, helped sustain its economic momentum. Our findings suggest that future crises may demand even more nuanced and sector-specific policy interventions. For instance, targeted support for small businesses and industries most affected by a downturn could provide a more efficient path to recovery. Additionally, policies aimed directly at consumers, such as mortgage relief programs, could prevent a cascade of defaults and stabilize the housing market more rapidly. A collaborative international response, leveraging the strengths of interdependent global economies, could amplify the efficacy of such measures. Therefore, we recommend a framework for economic policy that emphasizes flexibility, targeted support, and global coordination to not only cushion against immediate shocks but also to lay the groundwork for sustainable, long-term growth.
Conclusion: Steering Through Economic Adversity
The financial crisis that shook the foundations of global economies in 2007-2008 also brought to light the critical role of proactive monetary and fiscal policies in navigating economic adversity. The United States, the United Kingdom, and China each faced unique challenges and responded with tailored strategies that reflected their economic philosophies and priorities. Despite the varied approaches, the shared objective was clear: to stabilize the financial system, stimulate growth, and restore confidence. The recovery of equity markets, the resurgence of foreign direct investment, and the gradual uptick in GDP growth by 2010 are a testament to the effectiveness of these interventions. This period of economic recalibration provided valuable insights into the intricate dance between government policy and economic health, insights that continue to shape economic strategies in our increasingly interconnected world.








