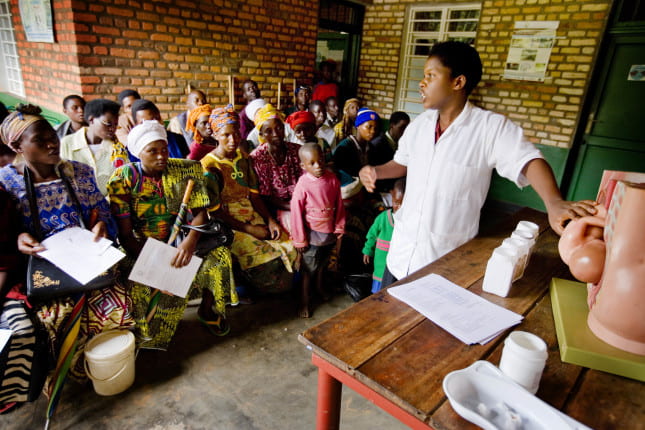

by ami31 | May 9, 2021 | Dashboard, Visualization
Childbirth is considered to be a landmark and joyous moment in any woman’s life. And although health experts say that no two childbirth experiences are the same, it is quite astounding that this can, in many cases, reach the extreme of death. According to statistics released by UNICEF, the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations Population Division, United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) and the World Bank Group, around 2.8 million pregnant women and newborns die every year of preventable causes [1]. This turns childbirth into an event to be feared as it poses a significant threat to the lives of many women across the globe. According to the United Nations’ , quality education is defined as one the of the seventeen sustainable development goals (SDGs), so how can education help mitigate childbirth mortality?
“Pregnancy is not a disease. It should not lead to deaths. Every maternal death should be regarded as an abnormality.” – Vivianne Ihekweazu, Director of the Nigerian Health Watch [2]
How are Childbirth Deaths Related to Education?
The World Development Indicators data from the World Bank [3] allows us to look into the impact of education on childbirth by exploring the percentage of births that are handle by skilled health staff. In the figure below, we plot the average life expectancy at birth in years with respect to the average percentage of births attended by skilled staff for each country. There is a clear positive correlation between the two variables. We therefore conclude that children who are delivered by skilled health workers during labor are more likely to have a higher life expectancy.
However, the impact of having educated people overseeing child delivery does not stop here. Unfortunately, carrying out child delivery without proper understanding of the necessary health procedures has more alarming implications. In the dashboard below, we notice a sharp decrease in both maternal mortality (women dying during labor) and neonatal mortality (newborns dying at birth) in countries where more childbirths are handled by skilled health workers. This implies that many of the childbirth related deaths can be attributed to the lack of necessary health skills.
Where are these Childbirth Deaths Mostly Occurring?
Below we find the places that suffer the most from this by selecting the countries that have a below average percentage of births attended by skilled staff.
By looking at the geographical distribution of these countries we unsurprisingly find that the majority is located in Africa. Furthermore, we notice that the educational attainment in these countries is significantly lower than countries that have more professionally handled childbirths. This is an expected causality since to have more skilled people perform childbirth procedures we need more educated people.
So the Solution Is, Educate More People!
“The benefits of education permeate all walks of life right from the moment of birth.” – Irina Bokova, Director-General of UNESCO [4]
In light of the above, we clearly need to have more educated people that are able to professionally handle childbirth procedures. This is especially needed in developing countries where childbirth mortality is more pronounced. A key approach strategy here is to educate the local birth attendants and community midwives that are already active in these communities. These local and community health workers are already more connected to the women and families in their towns making their newly found skills more accessible and allowing them to spread health awareness to pregnant women in their communities [5]. Finally some communities in rural Africa are located in remote locations faraway from any medical supply and service centers. Therefore, setting up portable medical outposts near these towns would greatly enhance the quality of services provided by birth attendants.
References
[2] E. Onyeji, “Despite having highest maternal mortality in Africa, Nigeria’s situation still underreported – Report,”
Premium Times Nigeria, 03-Dec-2020. [Online]. Available:
https://www.premiumtimesng.com/news/headlines/429266-despite-having-highest-maternal-mortality-in-africa-nigerias-situation-still-underreported-report.html.
[3] https://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/
[4] “Education can save lives, help reach sustainable development goals – UN agency,”
UN News, 18-Sep-2014. [Online]. Available:
https://news.un.org/en/story/2014/09/477702-education-can-save-lives-help-reach-sustainable-development-goals-un-agency.
[5] D. Shikuku and C. Ameh, “Investing in midwifery training and education for improved maternal and newborn outcomes,”
On Medicine, 19-Mar-2021. [Online]. Available:
https://blogs.biomedcentral.com/on-medicine/2021/03/19/midwifery-training-education-maternal-newborn-outcomes-isrctn/.

by Samar Eid | May 6, 2020 | Dashboard, Visualization
“When you carry a life and it’s there, and then gone, a part of your soul dies. Forever”. Casey Wiegano
Yes, I’m a mom, and just thinking about it for a fraction of a second breaks my heart! Unfortunately, Sub-Saharan countries along with some South Asian countries which are highlighted with darker blue in the map whiteness the highest infant mortality rates. In Sub-Saharan countries ,on average, 68 infants die in every 1000 births and this rate is the second highest among the classified regions (second graph)

From the bottom graphs, we can see that there is a high correlation between the average adolescents fertility rates and the female adolescents who are out of school. On the other hand, a correlation exists between the adolescents fertility rate and the mortality rate of infants.The highest rates are also observed in Sub-Saharan countries (darker blue).
Putting these observations into one sentence, we can infer that the more adolescent females that are out of school the more likely they are to give birth to infants that have higher chances of dying.
As such, female students in Sub-Saharan countries should be empowered. They should be encouraged to continue their education aiming to lower their fertility rates and indirectly lower infants mortality rates. With no doubt, many other factors should be considered such as improving healthcare systems for both, moms and children.

by Ghida | May 5, 2020 | Dashboard, Visualization
Females in the Arab World are always faced with discriminatory situations in a ‘professional environment’. From personal questions in an interview to on-the-job obstacles, something always has to remind us of who we are and how anchored we are to it. It is not very different around the world, however, females have only recently started to break through the notions of the ‘working man’, proving that the only professional difference between them is inside the minds of those who believe it exists.
When I started exploring the World Development Indicators data on Tableau, I could not but stop at the Employment to Population Ratio. So I developed a dashboard visualized below.

As seen on the map, there are big differences in Female Employment to Population Ratios around the world. Looking deeper into the ratios of 2 adjacent but very different cultures, the European Union and Arab Countries – the line graphs to the right -, we can notice the difference in the gaps between female and male ratios. While the Male Employment to Population Ratio is almost the same across both areas, there is a big difference in the female’s numbers, of course affecting the total ratios.
I believe the needed change starts in education – not only that of little girls who need to be equipped by the time they can join the workforce, but also of societies to be welcoming, and supportive of those girls. Many forces enter in this journey, in many cases education is an unaffordable luxury, which is why the intrusion of governments and NGOs is highly needed.
The featured image is from Aptology.

by Jad Rizk | May 5, 2020 | Dashboard, Visualization
The below storyboard highlights and examines a correlation between the GDP per capita and population age distribution. The visualization shows a comparison between regions and across time. This correlation makes us think more about future problems like pensions, economic growth, child labor, retirement age, and possible social problems. It is worth examining further if there is causality. Are economic changes coming based on age distribution?
The dashboard is interactive. Please feel free to filter, highlight, and discover the data in more depth. The fullscreen setting will allow for a better viewing experience.
by Tarek El khayat | May 4, 2020 | Visualization
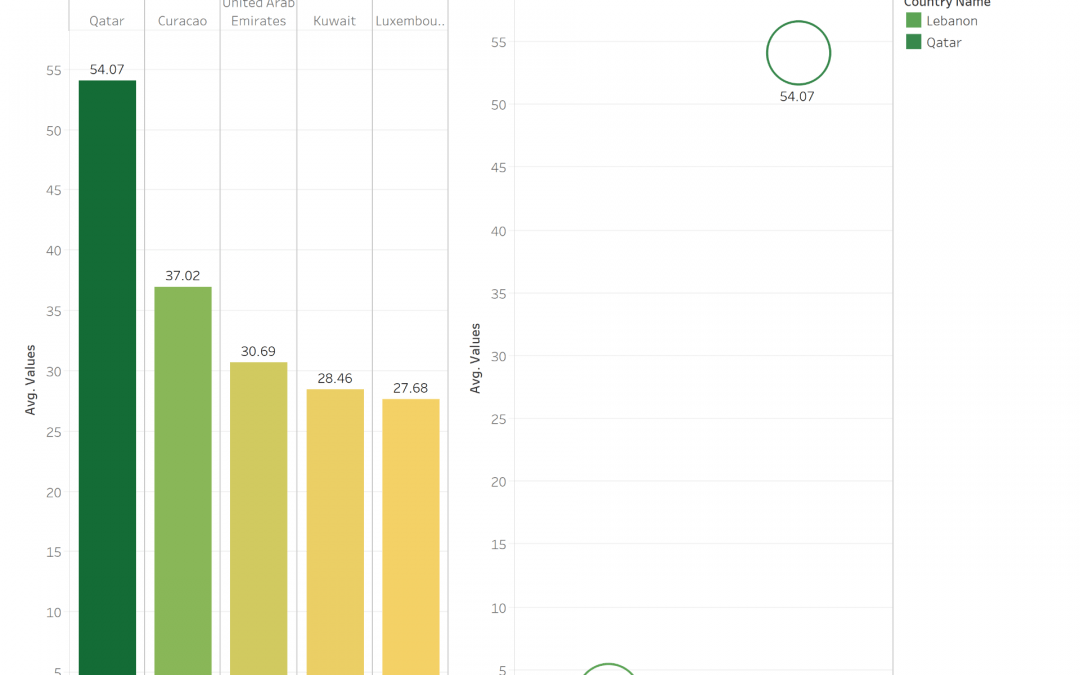
CO2 emission is one of the important factor that is destroying our planet and causing diseases, global warming …
The Graph shows the Top 5 countries with higher CO2 Emission and shows that QATAR take the lead in the world and the Arab region






