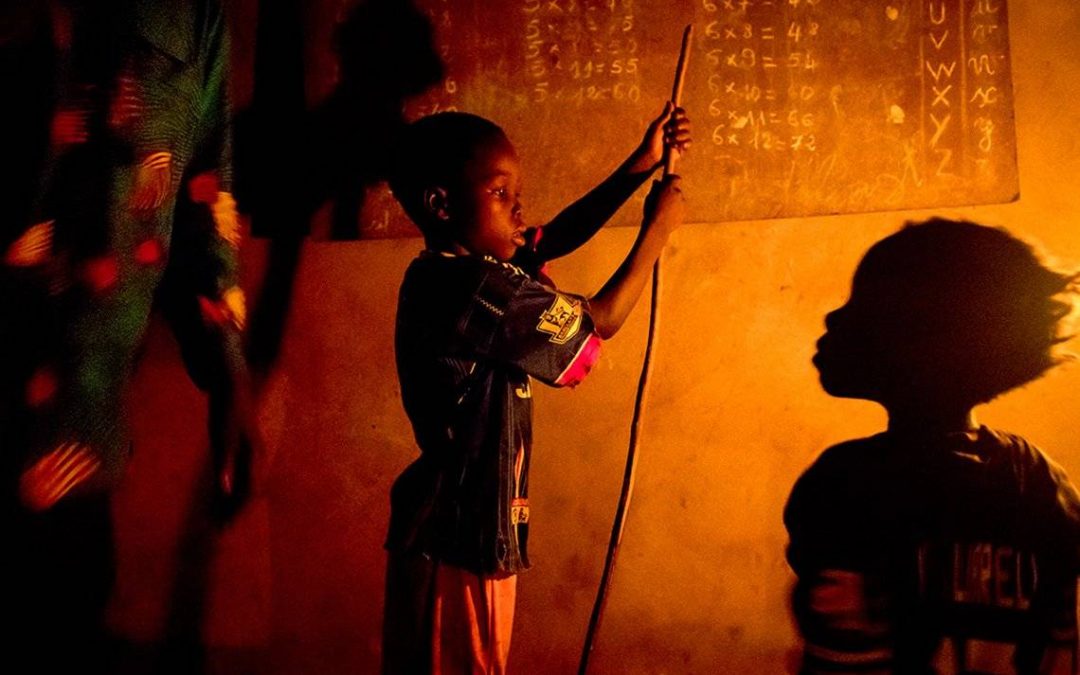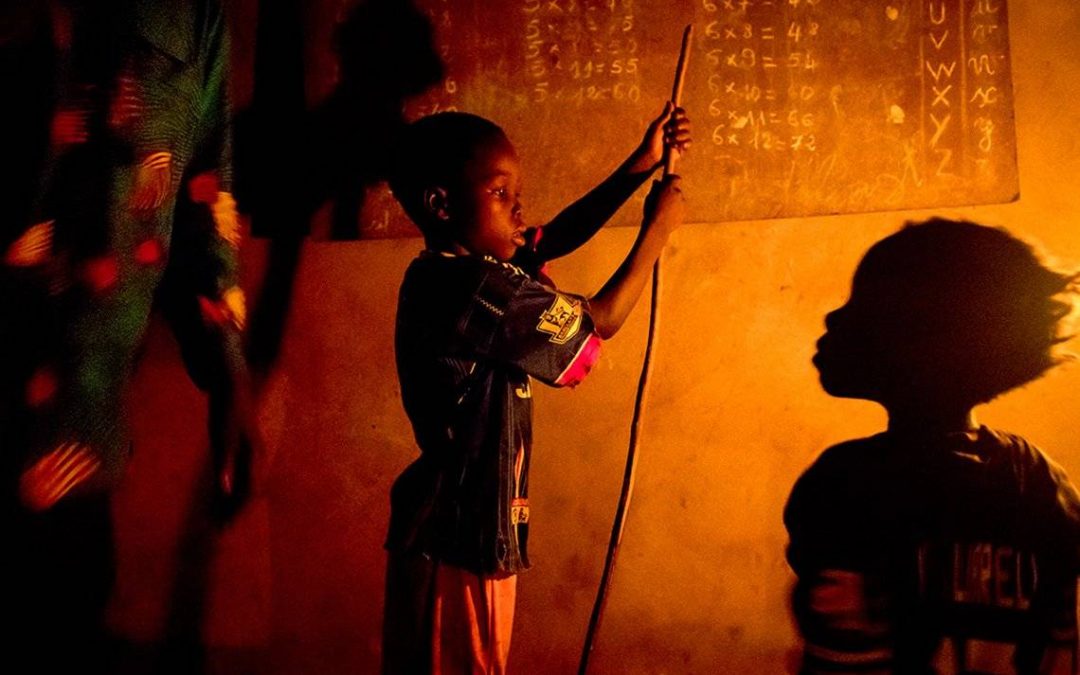
by mme129 | Apr 15, 2022 | Dashboard, Visualization
In the 21st century, most citizens across the world have access to electricity. According to The International and National Law Policy, access to electricity is considered as a human right. However, there are still countries far from having electricity. The World Energy Outlook in 2016 reported that around 1.2 billion people (16% of world population), where 90% of those live in Africa, have no access to electricity. The population of the African continent is a home for almost to a fifth of the world population, whereas it accounts to less than 4% of global electricity use.
Lack of electricity hinders the provision of basic services. More than half of schools and clinics in Africa remain without power or reliable electricity. In addition, electricity is essential since in numerous cases it means the difference between life and death. For example, hospitals need electricity to activate respiratory machines for people with respiratory illnesses. A research reports that around 4 million women and children die because lack of electricity every year compared to 1 million by HIV.
Moreover, a study reports that the number of people with access to electricity has increased worldwide, yet in Sub-Saharan Africa the number of people without access increased from 74% to 77% before 2019. Through out the 21st century, non-African countries that had low access to electricity for their citizens had an improvement and increased its percentage, whereas African countries remained with low access showing no improvement.
The African continent has the ability to generate solar electricity for the whole world in only a small portion of its land, almost a small part in the Algerian desert. Therefore, it is easily possible to increase the access to electricity for all African citizens, however it only needs some radical reforms. This is a long process due to the control of EU colonizers and the presence of corrupt politicians in almost all African countries.

by Salem G. | Apr 14, 2022 | Dashboard, Visualization
Suicide is something no one wants to talk about, the majority of people who are feeling down don’t openly talk about it. The highest population that is being affected are countries that are surrounding Russia, and in South Africa. There are 800k people commit suicide each year, this is due to many economical issues in these countries. Imagine Karim a husband and a father of 2 living in a country where the basic human needs are neglected. Now Karim is struggling to find a job due to the high unemployment rate, this means he is not able to feed his wife and kids. Imagine being in his place in a country with a 26% unemployment rate. People that are unemployed have a higher chance of commit suicide due their mental health taking a hit this could spiral own a dark hole which is hard to come out off. Unemployment forced 40% of the population to suffer from severe or moderate food insecurity and this is the disruption of food intake or eating pattern due to the lack of money and other resources. Now Karim can’t just feed his family but also can’t get the basic human needs.
All these problems correlate strongly with the Social protection and Labor Programs when these programs are lacking the result were higher suicide mortality rate. These programs help the population in managing risks and protect them from food insecurities through various methods. Poland has a high social program and the results of the suicide mortality rate is significantly lower compared to Lesotho which is the opposite with high suicide rates and low social program . This indicates to lower suicide rates we must increase the aid to the population by offering labor market, unemployment benefits, and other programs. Now Karim can relax and calm down as help is on its way to assist him and other people who are in need.

by gwk01 | Nov 23, 2021 | Visualization
It was 11:00 am on a Monday when I saw a nine-year-old boy, Bilal, lifting heavy rocks in a construction site. How many Bilals, children who toil long hours for a low wage, deprive themselves of education, and endure frequent violence and abuse just to financially support their families, do we meet daily?
Based on a study conducted by the Lebanese ministry of labor in 2013, there are almost 180,000 children working in Lebanon. Today, Lebanon is experiencing a huge decline in its gross domestic income (GDI). GDI is an economical metric that showcases the nation’s social welfare, and its deterioration results in more people living below 50% of the median income, and vice versa.

Thus, poverty is increasing in Lebanon, and more children as Bilal are being robbed of their childhood. The Lebanese government and supporting international organizations can take many initiatives to save Bilal and his friends; however, not all might have a fast and radical impact on the children labor phenomena. While observing international cases, through World Development Indicators dataset, I noticed that countries, which most of their population have access to electricity, have a lower percentage of poverty; thus, a lower number of employed children, and vice versa.

When power resources are available to the nation, people will have access to technologies, especially the internet. There are numerous internet usages that can create life opportunities for the individuals; for example, Bilal can access the internet to enroll in educational programs.

Considering the above, I appeal to the government and concerned institutions to utilize all their endeavors in providing a sustainable electrical solution for our children to live a “normal” life and have the chance to prosper.

by Sara Harba | Nov 21, 2021 | Uncategorized
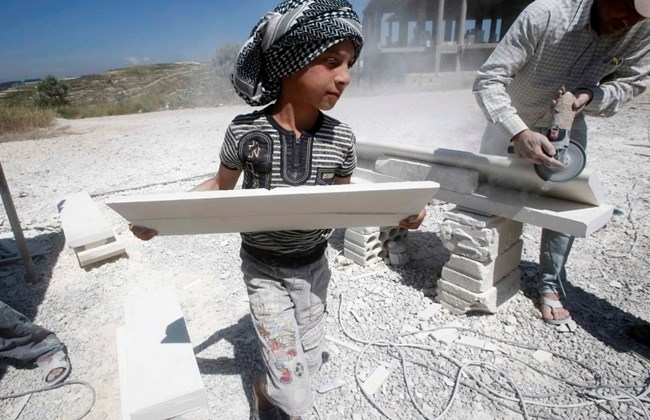
Many children in the Middle East and North Africa are deprived of education. Throughout the years, almost 18 % of adolescents and children were out of school on average in the region, which is the highest across East Asia, Europe, and Latin America.
 This is especially true for females who recorded higher average of dropout rates than males by 2.2% in the region over the years.
This is especially true for females who recorded higher average of dropout rates than males by 2.2% in the region over the years.
 The increase in dropout rates is due to several reasons and poverty plays a major role in increasing the rates of children out of school. It is evident that rates of people who make $1.90 per day has been increasing since 2013 in the Middle East, making it hard for parents to afford education expenditures for their children such as tuition fees and school supplies.
The increase in dropout rates is due to several reasons and poverty plays a major role in increasing the rates of children out of school. It is evident that rates of people who make $1.90 per day has been increasing since 2013 in the Middle East, making it hard for parents to afford education expenditures for their children such as tuition fees and school supplies.
 This leads families to pull their children out of school in order to work and help the family during financial hardship. As there is a positive linear relationship between children who are out of primary school and children employment, when the average rate of children out of school increases, the rate of children’s employment increases.
This leads families to pull their children out of school in order to work and help the family during financial hardship. As there is a positive linear relationship between children who are out of primary school and children employment, when the average rate of children out of school increases, the rate of children’s employment increases.

Furthermore, the norm that females are not supposed to work is enhancing the idea that females do not need to learn as they will not be able to participate in employment. This is encouraged by the average ratio of female to male participation in the labor force which is 33.09 below the average rate across all indicated regions.
 Therefore, it is important to bridge the gap of poverty to ensure that people can have sufficient funds to be able to send their children to school. This can be done by providing financial aid dedicated to school fees and supplies. That is because lower poverty rates indicate lower dropout rates among children since there is a positive relationship between the two.
Therefore, it is important to bridge the gap of poverty to ensure that people can have sufficient funds to be able to send their children to school. This can be done by providing financial aid dedicated to school fees and supplies. That is because lower poverty rates indicate lower dropout rates among children since there is a positive relationship between the two.

Moreover, it is important to raise awareness of the effects of dropping out of school on the future of children. Because the higher the average of adolescents out of school the more likely they will be considered as vulnerable employees in the future, which in turn lead them to be used and manipulated by employers.

Additionally, the higher the average rate of people completing at least a Bachelor degree, the higher the rate of salaries and wages. This means that if children where to stay in schools, they will be able to get higher salaries, which will provide them with a more stable future.

All the above factors are important in guaranteeing a better future for children. However, it is recommended that they be accompanied by the right laws that prevent child employment and provide equal opportunities for females to participate in the workplace.

by Jaafar Hoteit | May 5, 2021 | Dashboard
It is important to continuously pursue equality among populations and improve standards of livings. However, the pandemic has hindered our progress towards a more sustainable standard of living. Approximately 150 million people will be pushed into poverty in 2021 due to the pandemic. The pandemic has already pushed 88 million to 115 million people into extreme poverty in 2020.
While short-term solutions are important, long-term solutions are key to continuous sustainability. There is a clear correlation between the share of a population that use internet and GDP per capita. Policy makers should consider providing easy accessibility to the internet for its benefits which include, easy access to free education, work and connections.
Although the relationship is a correlation and not a causality, there still remains a conceptual understanding that investing into people will allow them to grow and invest back into their country’s economy. Accessibility to the internet can be a long-term solution towards sustainability!