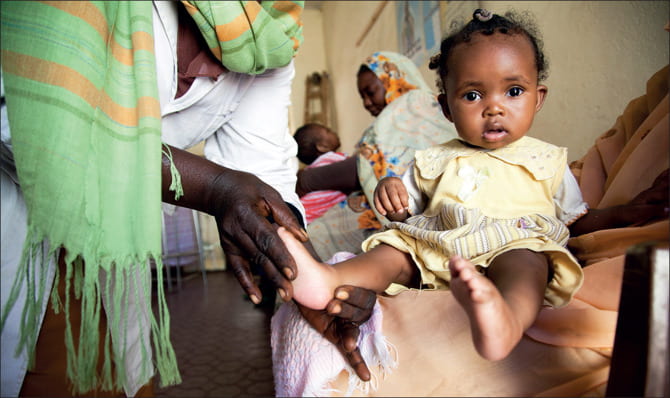
by rss64 | Nov 19, 2023 | Uncategorized
From the year 2000 to 2020, the health narrative of Nigeria’s children is evident through several vital indicators.
Our first indicator is life expectancy at birth. The numbers ranging between 47 to 52 years is significantly below the global average at 72.27 years. This not only reflects the health of newborns but also unveils the challenges within Nigeria’s healthcare system.
While infant mortality rates have declined from 109.6 to 72.3 per 1000 births, each data point signifies a story, a potential turning point for their healthcare policies.
A nation’s commitment is mirrored in its investment. The graph on health expenditure as a percentage of GDP is at an average of 3 to 5% across the years. However, for a cause as important as children’s well-being, this sliver of the budget is too small.
Immunization is a shield against preventable diseases. Positive trends in DPT and measles vaccination among infants aged 12 to 23 months emerge, yet the figures, standing at 56% for measles and 59% for DPT, flag an issue. Increasing immunization is a pivotal solution for decreasing infant mortality in Nigeria.
These graphs, urge us to strive for positive transformations. Each child deserves the chance to lead a healthy life. It starts with shifts in governmental expenditures and efforts from NGOs, ensuring free immunization for all children. Our journey towards a healthier country is rooted in understanding these trends and collectively working toward a future that every child deserves. Let’s turn these graphs into blueprints for a healthier tomorrow.

by cth07 | Nov 19, 2023 | Uncategorized
by Charbel Hanna Daou (MSBA 24)
In the heart of the Caribbean, Jamaica faces a startling reality: its soaring intentional homicide rate is not just a statistic, but a looming shadow over the nation’s future. This crisis goes beyond mere numbers, threatening the very fabric of Jamaican society and shaking the pillars of stability and safety that its citizens rely on. It’s a call to action, demanding not just attention, but a deep dive into the root causes and a strategic battle plan to turn the tide against this wave of violence. The urgency to address and mitigate this issue couldn’t be more pressing, as the fate of Jamaica’s well-being hangs in the balance.
Delving into the Crisis
The alarming rise in Jamaica’s homicide rates over the past two decades is a cause for serious concern. The data shows an increase to 52.1 homicides per 100,000 people by 2021, a figure that not only stands out in the Caribbean region but also ranks highest on a global scale. This disturbing trend is indicative of deeper societal and systemic issues that need to be addressed with urgency and precision.
Strategic Approaches Aligned with SDGs
In response to this escalating crisis, two potential strategic solutions, in alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), present themselves as viable pathways to combat the high homicide rates:
- Increasing Government Health Expenditure (Aligned with SDG 3): This strategy focuses on the crucial role of health in society. By boosting government spending on health care, particularly in areas like mental health services and addiction treatment, Jamaica could tackle some of the underlying factors contributing to the high rate of homicides. The premise here is that better access to health services, including mental health care, can play a significant role in preventing violence and crime.
- Extending the Duration of Compulsory Education (Aligned with SDG 4): Education is a powerful tool for social change. By increasing the years of compulsory education, Jamaica could address several root causes of crime, including poverty and inequality. Education not only equips individuals with knowledge and skills but also opens up opportunities, promoting social mobility and reducing the likelihood of individuals engaging in criminal activities.
Learning from Global Experiences
The experiences of the Russian Federation and Colombia provide valuable lessons. Both countries have demonstrated a correlation between enhanced health expenditures, extended compulsory education, and a decrease in intentional homicides. In contrast, Jamaica’s relatively stagnant approach in these areas might be contributing to its high homicide rates. This comparison suggests that adopting similar strategies could yield positive results in Jamaica.
Government of Jamaica, Here’s What You Should Do
Given the evidence and the success of similar strategies in other countries, the following recommendations are proposed for Jamaica:
- Increase Health Expenditure: A substantial increase in health expenditure per capita, specifically by a minimum of $100, could significantly improve the quality and accessibility of health services. This step would not only address immediate health concerns but also contribute to the long-term goal of reducing violence and crime.
- Reform Education Policies: Strengthening and reforming education policies to extend the duration of compulsory education to at least 12 years is crucial. This change would have far-reaching effects, not only in educating the populace but also in providing them with better opportunities and reducing the likelihood of them resorting to crime.
In the face of its daunting homicide rates, Jamaica stands at a crucial crossroads. The journey ahead is challenging, but it’s also filled with opportunity. By adopting innovative strategies like increasing health expenditure and extending compulsory education, Jamaica isn’t just fighting crime; it’s reinventing its future. This bold move towards enhancing healthcare and education could be the key to unlocking a new era of peace and stability. Imagine a Jamaica where every citizen is empowered by knowledge and supported by a robust healthcare system. That’s the vision—a safer, stronger Jamaica, thriving in harmony and moving confidently towards a brighter tomorrow.

by zoh00 | Nov 19, 2023 | Uncategorized
Employment in Iceland and Saudi Arabia can be understood through various factors, including the labour market, workforce participation, employment sectors, and government policies.
An increase in 2020 and 2021 in Saudi. This may be due to several factors. Historically, the majority of the labour force in Saudi Arabia has been made up of expatriate workers. The government has introduced policies to reduce this dependency and create job opportunities for Saudi citizens.
An increase in female employment rate from 2018 till 2021 in Saudi while Iceland maintains a steady rate .This may be due to recent reforms such as:
- allowing women to drive
- expanding their employment opportunities,
- The government target to increase women’s participation in the workforce,
- various sectors are gradually opening up to women.
While Iceland is known for promoting gender equality in the labour force, this steady rate is a result of various policies and initiatives aimed at promoting gender equality in the workplace.
Saudi Arabia’s Effort towards gender equality are well noticed over the last few years, and Iceland is a known for its gender equality in the labour force. but will it be reflected in these countries when navigating wages by gender???

by gsm13 | Nov 19, 2023 | Uncategorized
In the unfolding narrative of global environmental challenges, the tale of the United States and China emerges as a compelling story of shifting roles and responsibilities in the battle against climate change.
The visual representation of CO2 emissions between the United States and China from 1990 to 2020 on a line chart underscores a critical environmental challenge. The problem lies in the discernible shift of emission supremacy between the two nations, with the USA leading until 2005, at which point China surpassed it. This transition is indicative of a broader issue: the need for a collective, global response to address escalating carbon emissions. The evidence is clear—the historical dominance of the United States in emissions, followed by China’s ascent—underscores the urgency of finding a sustainable solution. The potential remedy to this issue requires a multifaceted approach. Firstly, international collaboration is paramount, necessitating joint efforts in clean energy initiatives, sharing technological advancements, and leveraging collective resources. Secondly, a focus on renewable energy sources, coupled with substantial investments in carbon capture technologies, is crucial. Additionally, stringent emissions regulations and their effective enforcement should be implemented, with governments playing a pivotal role in setting and monitoring emission reduction targets. A comprehensive solution also involves public and private sectors prioritizing sustainability, embracing energy-efficient practices, and fostering innovation. In conclusion, the story depicted by the line chart serves as a clarion call for immediate and concerted action. Recommendations include fostering global collaboration, prioritizing renewable energy, implementing robust regulations, and cultivating a collective commitment to a sustainable future—a future where the line chart reflects a downward trend in CO2 emissions for both the United States and China.

by kam42 | Nov 19, 2023 | Uncategorized
This interactive visualizations offer detailed comparison of governance, economic conditions, and social stability in Canada, Saudi Arabia, and Syrian Arabic Republic from 2003 to 2021. The analysis begins with a look at corruption control, where Canada exhibits consistent strength in governance. This is visually represented in our map by lighter regions indicating lower inflation, emphasizing Canada’s economic stability. Where also in the third visual, it is shown the absence of terrorism and violence acts.
Turning to Saudi Arabia, its control of corruption is less stringent compared to Canada. This is reflected in the map, where Saudi Arabia is depicted with a darker color than Canada, indicating higher inflation rates. Additionally, in our bar chart analysis of the absence of violence, Saudi Arabia falls into the negative region, suggesting the presence of some violence and instability.
The situation in Syria, especially after the war began in 2011, shows a stark difference. Governance control deteriorates , mirrored by the country’s severe inflation and diminishing peace and stability. The map distinctly shows Syria in darker shades, signifying high inflation levels. Furthermore, in the bar chart measuring the absence of terrorism and violence, Syria is deeply entrenched in the negative area, highlighting the extensive violence and unrest prevalent in the country.
Through this comparative study, we delve into how governance quality is intricately linked to economic health and societal peace. Our findings resonate with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 16, which advocates for peaceful, just, and strong institutions. This analysis not only sheds light on the varying situations in these three countries but also emphasizes the critical need for governance systems that nurture economic and social stability, crucial for achieving sustainable development as envisioned in the SDGs by 2030.

by msh57 | Nov 19, 2023 | Uncategorized
Saudi Arabia Economic Diversification
KSA’s Sharp GDP Drop
´In 2020, Saudi Arabia experienced a significant drop in its Gross Domestic Product (GDP), primarily due to the dual impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and a sharp decline in global oil prices since Saudi Arabia is a major oil-producing country, and its economy is heavily dependent on oil exports whre the global oil market experienced a sharp decline in prices due to a combination of factors, including reduced demand during the pandemic and a price war between major oil-producing nations.
´The above plot shows the sharp GDP drop from 840 billion dollars in 2019 to 730 billion dollars in 2020. According to several Saudi Arabia’s government, this was due to the decline of global oil prices.
Potential Solution
´The Solution is Diversifying the Saudi economy away from its heavy reliance on oil and investing in non-oil sectors like tourism, technology, and manufacturing and other sectors, Thus approaching the problem of GDP discussed, the government decided to invest in a non-oil sector that is the industrial sector and increase the manufacturing rate of several products which aims to diversify the economy of Saudi Arabia instead of only depending on oil and gas production.
KSA goverment invested in manufacturing such as petrochemical complexes: development of petrochemical complexes that can produce a wide range of products, including plastics, fertilizers,…
´This plot shows the increase in the manufacturing value from 93 billion dollars in 2020 to 163 billion dollars in 2022 after increasing the investment in this industry.
Findings
´After 2 years of applying diversification and investing in a non-oil industry we noticed a sharp improvement in the gross domestic product(GDP) which highlights the importance of the initiative we took.
Solution Validation
The Dashboard below shows that the solution proposed was a direct cause for GDP increase between 2020 and 2022.
Conclusion
Economic diversification is a multifaceted process that offers numerous advantages, including increased resilience, job creation, and sustainable development. While challenges exist, the potential long-term benefits make diversification a valuable strategy for countries seeking to build robust and adaptable economies





