
A measured approach to ending poverty and boosting shared prosperity
#SDG1 : NO POVERTY
#SDG8 : Decent work and economic growth
Most countries in the Arab region are witnessing high rates of poverty due to the poor management held by its authorities. There’s lack of economic development which is directly affecting the situation in each of the countries. There are several reasons behind delaying the growth of the economies and one of them is not understanding the real purchasing power of the consumer. In order to better understand it , countries should start evaluating their gross domestic product based on purchasing power parities rather than exchange rates.
What are purchasing power parities?
Purchasing Power Parities measure the amount of currency needed in a certain country to buy the same basket of goods and services that a single unit of another country’s currency can buy. PPPs make it possible to compare the output of economies and the welfare of their inhabitants in real terms, thus controlling for price level differences across countries.
PPPs are used for analysis and measurements in many areas by a wide variety of users, ranging from international organizations to policymakers, academia and the private sector. Due to significant differences in price levels across countries, market exchange rate‐ converted GDP does not accurately measure the relative sizes of countries or the levels of material well‐being. For this reason , we can see how the illogical health care, education and living costs in the countries are leading to poverty and unfortunate productivity.
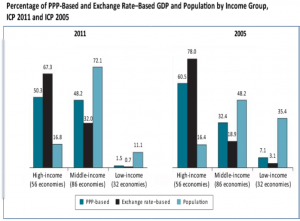
In the below visualizations we can see how the income gaps between countries have been narrowed after observing the results in 2005 and in 2011.
Moreover, in the below visualization, we can see that Egypt surpassed Saudi Arabia in having the largest economy in 2020 when we compared GDP based on PPPs.

% change of GDP based on PPP between 2017 and 2020

We can see also that Egypt witnessed the highest % change in GDP with 17.63 % while Sudan observed a major decrease by 19.75%.
Recommendations:
Countries should use PPPs because it allows them to analyze their income or consumption data in globally-comparable terms by taking account of the purchasing power differences between countries.
Without PPPs, comparisons of income and consumption levels would typically rely on market exchange rates, which generally underestimate the purchasing power of consumers in poorer countries, making them appear too poor relative to those in richer countries, compared with the real differences in their living standards.
Use PPPs to set a real poverty line which describes the real deprivation level of the individual . This person is considered poor if his or her income or consumption falls below this line.