
by aab75 | Nov 18, 2023 | Visualization
In light of recent events, we delved into a pressing issue: the unsettling fluctuations in mortality rates in Lebanon. It was evident that these shifts had deeper roots, impacting lives and reflecting significant historical events.
The data painted a stark picture. Between 1975 and 1990, Lebanon witnessed a devastating surge in mortality rates, reaching a staggering 31.17. The Lebanese Civil War cast a long shadow, leaving behind a legacy of loss and devastation that echoed in the mortality records.
Post-1990, there was a semblance of stability with mortality rates hovering around 4-5, despite intermittent spikes like the one in 2006 during the July War. It seemed like a fragile peace amid lingering echoes of conflict.
Then, at the dawn of 2019, another dramatic shift occurred. The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic jolted mortality rates sharply upward once more. It was a distressing reminder of how swiftly external factors could disrupt the delicate balance of life.
Contribution to SDG
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being: The significant increase in mortality rates during the Lebanese Civil War, subsequent fluctuations due to regional conflicts like the July 2006 war, and the sharp increase attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic highlight the importance of SDG 3. It emphasizes the need for resilient healthcare systems, disease prevention, and access to quality healthcare, especially during periods of conflict and health crises.
SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions: The impact of the Lebanese Civil War and regional conflicts on mortality rates underscores the relevance of SDG 16. Ensuring peace, stability, and strong institutions is vital to prevent the adverse effects of conflicts on public health and to establish systems capable of effectively managing crises and their aftermath.
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities: The fluctuations in mortality rates due to historical conflicts and the COVID-19 pandemic might reveal disparities and inequalities in healthcare access, response, and resilience. Addressing SDG 10 involves reducing these disparities, ensuring equitable access to healthcare services, and mitigating the disproportionate impacts of crises on vulnerable populations.
by Youssef Daouk | May 4, 2020 | Visualization
This visualization shows the comparison of the dependency ratios of old age as well as children between several middle eastern countries.
It is seen that the child dependency ratio is not that high in Lebanon, but we chose to focus more on the old-age dependency. As seen in the visualization above, Old age dependency in Lebanon is 10.08, which is neither the best nor the worse in comparison to others in the region. But the good thing is that the elderly are still active in the economy, this can help boost the economic state in Lebanon if treated properly.
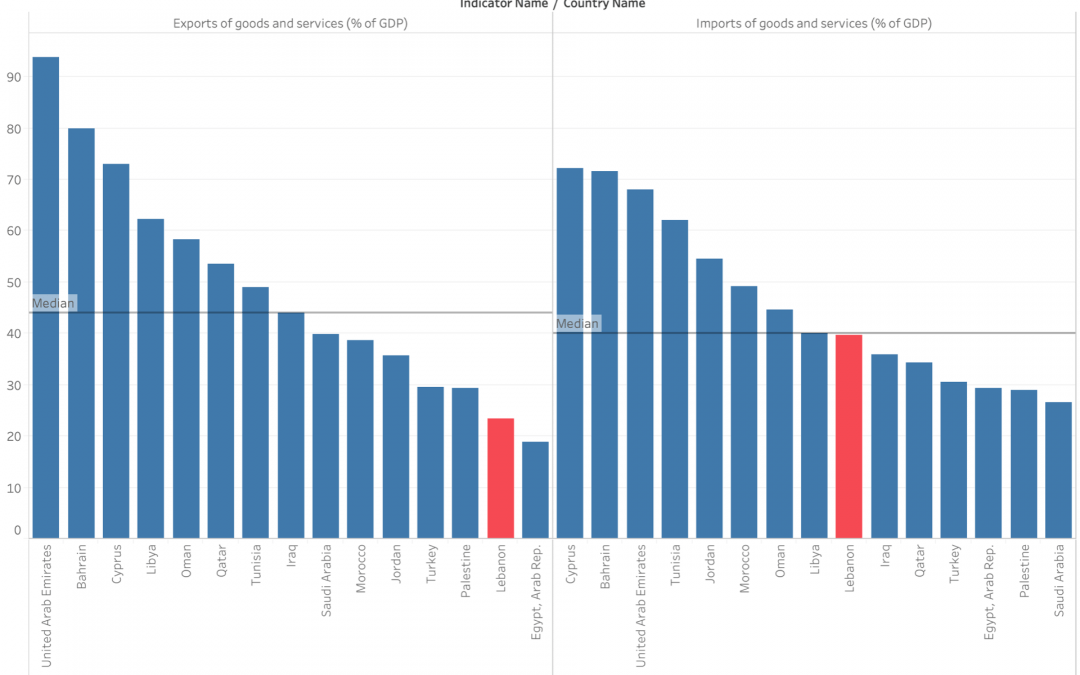
by Sari Hajjar | May 4, 2020 | Visualization
The poor economic situation in Lebanon is the result of multiple problems that led the this crisis. One of those problems is the imbalance of the exports and imports of goods and services in percentage of the country’s GDP.
It is clear that Lebanon has an export deficiency problem, with a percentage of imports double the percentage of exports, which is in turn way below the region median.

